Introduction to RMM for Internal IT Departments
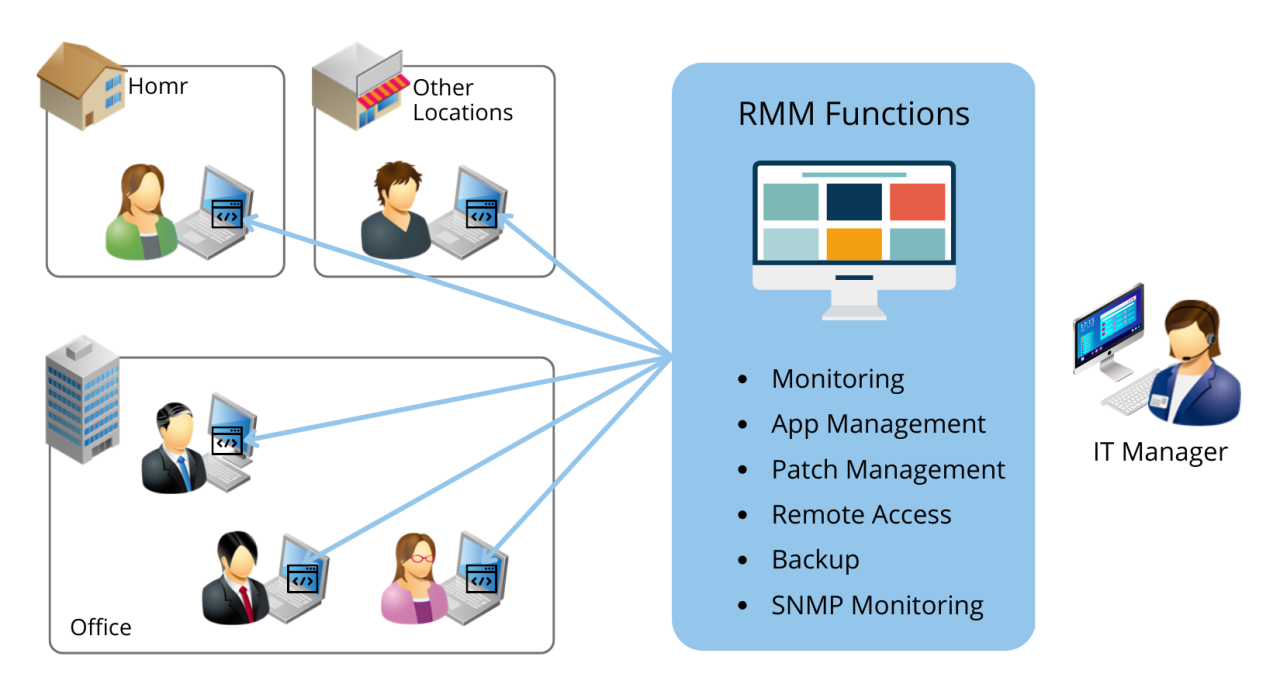
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software provides a centralized platform for IT teams to manage and monitor computer systems, servers, and other network devices remotely. It streamlines IT operations, allowing for proactive maintenance and quicker issue resolution, ultimately improving overall efficiency and reducing downtime.
Core Functionalities of RMM Software
RMM software offers a suite of tools for managing various IT assets. Key functionalities include remote control, software deployment, patch management, and system monitoring. These capabilities allow IT staff to address issues swiftly and ensure consistent system performance across the organization. This streamlined approach saves valuable time and resources.
Benefits of Using RMM Software
Implementing RMM software in an internal IT department yields numerous benefits. Proactive monitoring reduces downtime by identifying potential problems before they impact users. Centralized management simplifies tasks like software updates and system configurations, boosting operational efficiency. Improved visibility into system performance allows for quicker issue resolution and more effective troubleshooting. The reduction in support tickets and resolution times translates into increased productivity.
Typical Use Cases for RMM in Internal IT
RMM software proves invaluable in various internal IT scenarios. One common use case is managing a large fleet of employee devices, ensuring consistent security patches and software versions. Another is handling server maintenance, enabling remote access and quick troubleshooting to minimize downtime. Furthermore, RMM can be used for automated backups, streamlining data protection procedures and minimizing data loss risks. A final application is the implementation of consistent security policies, monitoring for compliance and mitigating potential vulnerabilities.
Key Features Comparison of Different RMM Solutions
| Feature | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Control | Allows IT staff to access and control remote devices. | Facilitates quick troubleshooting and configuration changes. | Security concerns if access isn’t properly secured. |
| Software Deployment | Automated installation and updates of applications across devices. | Saves significant time and ensures consistent software versions. | May require specialized knowledge for complex deployments. |
| Patch Management | Automated application of security patches to devices. | Minimizes vulnerabilities and enhances security posture. | Potential for conflicts with existing software or configurations. |
| System Monitoring | Real-time tracking of device performance and resource usage. | Early detection of potential issues and proactive maintenance. | Data overload can make it challenging to interpret vast amounts of information. |
Implementing RMM Solutions in Internal IT
Implementing a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution within an internal IT department streamlines management tasks, enhances security, and improves overall efficiency. A well-integrated RMM system can proactively address potential issues, reducing downtime and improving response times to incidents. This detailed guide will Artikel the steps involved in selecting, configuring, and integrating RMM software into your existing infrastructure.
Choosing the right RMM solution requires careful consideration of your specific needs. Factors such as the number of devices, complexity of the IT infrastructure, and budget constraints all play a role in the selection process. A thorough evaluation of available solutions, including their features, pricing, and customer support, is essential before committing to a particular vendor.
Selecting an Appropriate RMM Solution
Selecting the right RMM solution is crucial for maximizing efficiency and effectiveness. A tailored solution will align with your IT department’s specific needs, providing the required features and support. Careful consideration of factors such as scalability, reporting capabilities, and ease of use is essential in this stage. Consider factors like the number of devices, the type of devices (desktops, laptops, servers, etc.), the required features (patch management, remote control, security monitoring, etc.), and the budget constraints.
Configuring RMM Software
Configuring RMM software involves setting up the software to manage your internal devices. This process includes adding devices, configuring remote access permissions, and establishing communication protocols. After the initial setup, the RMM software will provide a centralized platform for monitoring and managing your entire fleet of devices. A step-by-step guide will be critical for successful deployment.
- Device Discovery and Inventory: The RMM software needs to identify and catalog all the devices within your network. This process is usually automated and provides an initial inventory of your IT assets. This helps in knowing the current status of the devices.
- Remote Access Configuration: Defining user permissions and access levels for remote control is crucial. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access and manage devices remotely. Security should be paramount.
- Software Deployment and Updates: Implementing software updates and deployments can be automated using the RMM. This minimizes downtime and ensures consistent software versions across the entire fleet of devices.
Integrating RMM with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating RMM with existing infrastructure is crucial for seamless operation. This involves configuring the RMM to interact with your current systems and processes. Consider the network architecture, existing security protocols, and user accounts. This step ensures that the RMM solution integrates smoothly into the existing environment.
Establishing Monitoring Schedules and Alerts
Monitoring schedules and alerts are essential for proactive maintenance and problem resolution. The RMM software should be configured to monitor devices, applications, and user activity for potential issues. The goal is to establish alerts that notify the IT team about any anomalies.
- Scheduled Scans: Regular scans ensure that devices are healthy and operating as expected. These scans detect issues early and prevent major problems.
- Alert Configuration: Customizable alerts provide notifications about critical events, such as device failures, security breaches, and performance issues. This ensures timely response to incidents.
RMM Implementation Process Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in implementing an RMM solution:
[Insert a flowchart image here. The flowchart should depict a process starting with needs assessment and ending with ongoing maintenance. Each step should be clearly labeled, including steps for selecting software, configuring it, integrating it, and establishing monitoring. The flowchart should be visually clear and easily understandable. It should include the stages for planning, installation, testing, and validation. Illustrate potential issues and solutions.]
Managing IT Assets with RMM
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software provides a powerful tool for tracking and managing internal IT assets. This allows IT departments to gain a comprehensive view of their infrastructure, improving efficiency and reducing downtime. By centralizing asset information, RMM solutions can streamline tasks like software deployment, patching, and troubleshooting.
Effective asset management is crucial for any IT department. RMM solutions enable a more proactive approach to maintaining the health and security of internal systems, leading to a more reliable and secure IT environment.
Tracking and Managing Internal IT Assets
RMM solutions offer robust tools for cataloging and tracking all internal IT assets, from desktops and laptops to servers and network devices. This detailed inventory helps IT staff quickly identify and locate specific equipment, reducing response times in case of issues. This inventory can include details like serial numbers, purchase dates, warranty information, and associated software licenses. Accurate asset tracking is vital for maintaining compliance and managing potential security risks.
Remote Device Access and Control
RMM software empowers internal IT teams to remotely access and control various devices within the organization. This capability allows for efficient troubleshooting, software deployment, and configuration changes without physically interacting with each device. This feature significantly speeds up the resolution of technical issues, allowing internal IT teams to focus on more complex problems. Remote control is crucial for ensuring prompt and consistent maintenance of the IT infrastructure.
Deploying Software Updates and Patches
RMM tools facilitate the automated deployment of software updates and security patches across the entire IT infrastructure. This automated process significantly reduces the time and effort required for manual updates, minimizing downtime and risks associated with outdated software. Scheduling and monitoring these deployments ensures consistency and minimizes disruption to daily operations. This approach also improves security posture by keeping systems up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Troubleshooting Internal Systems
RMM solutions offer advanced diagnostic tools for quickly identifying and resolving issues with internal systems. Real-time monitoring and reporting capabilities allow IT teams to proactively address potential problems before they impact end-users. The remote access capabilities integrated with diagnostic tools can aid in troubleshooting by providing insights into the system’s health and configuration. This proactive approach significantly reduces the frequency and impact of IT outages.
Comparison of RMM Asset Management Tools
| Tool | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| ManageEngine Desktop Central | Comprehensive asset tracking, remote control, patch management, and reporting | Robust feature set, extensive reporting capabilities, good for large organizations. | Can be expensive, learning curve may be steep for smaller teams. |
| SolarWinds RMM | Extensive device monitoring, remote control, and automation features. Strong integration with other SolarWinds products. | Powerful features, strong automation capabilities, good for organizations with a large IT infrastructure. | Can be expensive, steep learning curve, may not be the best fit for small businesses. |
| ConnectWise Manage | Excellent remote support capabilities, strong integration with other ConnectWise products. | Wide range of support options, flexible pricing options, good support resources. | Interface might be less intuitive compared to other options, limited reporting features. |
| Autotask PSA | Robust asset tracking, remote management, and reporting. Excellent for managing complex IT infrastructure. | Scalable, versatile, robust support, integrates with other Autotask products. | Pricier compared to other solutions, more complex to implement for smaller teams. |
Security Considerations with RMM
Remote Management Solutions (RMM) offer significant advantages for internal IT departments, but implementing them necessitates careful consideration of security implications. Proper security measures are crucial to protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access and malicious activities. A robust security posture within the RMM environment is paramount for maintaining a secure IT infrastructure.
Security Implications of RMM Implementation
Implementing RMM involves granting remote access to IT staff and potentially third-party vendors. This introduces a higher level of risk if security protocols are not meticulously designed and enforced. Failure to address potential vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, system compromise, and financial losses. Therefore, comprehensive security measures are essential for mitigating these risks.
Secure Authentication and Access Control
Strong authentication mechanisms are critical for controlling access to the RMM system. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is highly recommended to add an extra layer of security. Strict access control lists (ACLs) should be implemented to limit access to specific users or groups, granting privileges only as needed. This granular control prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data or making modifications to critical systems. Robust password policies, including complexity requirements and regular password changes, are also essential.
RMM and Data Integrity/Compliance
RMM solutions play a vital role in maintaining data integrity. Regular backups and version control features can help restore systems to a previous state in case of data loss or corruption. Compliance with industry regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) often mandates specific data protection measures. RMM solutions should be configured to adhere to these standards. Furthermore, the RMM should track and log all actions performed within the system, enabling audits and investigations in case of incidents.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities in RMM Systems
A poorly configured RMM system can introduce several security vulnerabilities. One significant risk is the use of default credentials, which can be easily discovered by attackers. Another vulnerability arises from inadequate patching of the RMM software itself. Furthermore, unpatched operating systems or applications on the managed devices create entry points for malicious actors. Finally, inadequate network security measures around the RMM server can expose it to external threats.
RMM Security Checklist
This checklist provides a framework for securing an RMM implementation.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users and enforce strong password policies.
- Granular Access Control: Establish clear access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access to specific resources based on user roles and responsibilities. Only allow necessary access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits of the RMM system and managed devices to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Software Updates: Ensure the RMM software, operating systems, and applications on managed devices are regularly updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Network Security: Implement strong network security measures around the RMM server to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Consider a dedicated, isolated network segment for RMM operations.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to address potential security breaches or vulnerabilities.
Reporting and Analytics with RMM
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software goes beyond basic device management. A key strength lies in its ability to generate comprehensive reports, providing valuable insights into system performance, utilization, and potential issues. This allows IT departments to proactively address problems, optimize operations, and ultimately improve the overall efficiency of their IT infrastructure.
RMM Report Generation, Rmm for internal it department
RMM solutions gather data from managed devices in real-time, creating a detailed picture of system health. This data includes CPU and memory utilization, disk space, application performance, and network traffic. This real-time monitoring enables the generation of reports on system performance and utilization, offering a comprehensive overview of the IT environment. Reports often visualize this data through graphs, charts, and tables, making it easily digestible and actionable.
Utilizing RMM Data for Trend Identification
RMM data is not just about snapshots; it’s about patterns. By analyzing historical data, IT departments can identify trends in system performance and utilization. For example, if CPU usage consistently spikes during specific hours of the day, it could indicate a bottleneck in an application or a need for additional server resources. Regularly reviewing these reports helps identify potential problems before they escalate into major outages or performance issues. Recognizing these trends enables proactive solutions, preventing future problems and saving time and resources.
Creating Custom RMM Reports
Many RMM platforms offer customization options for generating reports. This allows IT teams to tailor reports to their specific needs, focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to their internal operations. For instance, an IT department might want a report that highlights the uptime of critical servers or the response time of specific applications. This level of customization is crucial for internal IT departments to focus on their unique needs and performance metrics. By selecting the specific data points needed, internal IT departments can gain a deep understanding of their environment.
Optimizing IT Operations with RMM Data
RMM data provides a wealth of information for optimizing IT operations. Monitoring data on software updates, patching schedules, and device compliance allows for a more efficient and proactive approach to managing IT infrastructure. This data can help to identify areas where processes can be streamlined or automated, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency. Understanding patterns in software usage and hardware performance empowers proactive decision-making, minimizing downtime and maximizing resource utilization.
Different Types of RMM Reports
| Report Type | Data | Purpose | Actionable Insights |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Performance | CPU, Memory, Disk I/O, Network Utilization | Identify bottlenecks, performance issues, and potential resource constraints. | Optimize resource allocation, identify underperforming systems, and plan for future upgrades. |
| Application Performance | Application response times, errors, and usage patterns | Monitor application performance, identify slowdowns or errors, and ensure optimal user experience. | Identify application-specific bottlenecks, recommend upgrades, and streamline workflows. |
| Security Compliance | Security patches, updates, and configurations | Ensure devices are compliant with security policies and identify potential vulnerabilities. | Proactively address security risks, automate patching processes, and maintain a strong security posture. |
| Asset Inventory | Hardware and software details, locations, and configurations | Track and manage IT assets, ensure accurate records, and maintain a complete inventory. | Identify outdated or underutilized assets, plan for asset replacement, and optimize asset allocation. |
Scalability and Future Considerations for RMM: Rmm For Internal It Department
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions are crucial for modern IT departments, enabling efficient management of diverse and growing IT infrastructures. Planning for future scalability is vital to ensure the RMM solution remains effective as the IT environment evolves. This section examines strategies for accommodating growth, integrating with other tools, and anticipating future trends in RMM technology.
RMM solutions offer flexibility in scaling to accommodate evolving IT needs. This adaptability is critical for maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness as the size and complexity of the IT infrastructure change. Proper planning for future upgrades and integrations ensures the RMM system remains a valuable asset for years to come.
Scalability of RMM Solutions
RMM solutions typically scale proportionally with the number of devices managed. Many platforms offer tiered pricing models that adjust based on the number of endpoints or users. This allows organizations to incrementally add more devices to the managed inventory as the IT infrastructure expands. The scalability aspect also extends to the increasing complexity of the IT infrastructure, including different operating systems and applications. Modern RMM solutions are designed to handle this diversity, often with extensive device profiles to accommodate different configurations.
Planning for Future RMM System Upgrades
Planning future upgrades proactively is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. A phased approach is often beneficial, starting with smaller upgrades to test compatibility and functionality before implementing wider changes. Regularly assessing the current RMM solution’s performance, identifying bottlenecks, and forecasting future needs are essential steps in the upgrade planning process. Thorough documentation of the existing system and its configurations is vital for a smooth transition during upgrades.
Integration with Other IT Management Tools
RMM solutions often integrate with other IT management tools, such as ticketing systems, vulnerability scanners, and configuration management databases. These integrations streamline workflows, improve collaboration, and provide a holistic view of the IT infrastructure. The ability to integrate with existing tools is a key factor in selecting an RMM solution. A robust API and well-documented integration processes are crucial for successful integration. For example, an integration with a ticketing system allows for automated alerts and streamlined issue resolution.
Future Trends in RMM Technology
Future trends in RMM technology often involve greater automation and AI integration. Predictive maintenance, automated patching, and AI-powered anomaly detection are emerging features that promise to reduce manual effort and enhance proactive IT management. Cloud-based solutions are also becoming increasingly popular, offering scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. This trend reflects the broader shift towards cloud-based IT infrastructure.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of RMM
The long-term cost-effectiveness of RMM solutions often surpasses the initial investment. Reduced downtime, improved security, streamlined workflows, and proactive maintenance contribute to significant savings over time. For example, preventing a major system outage can save a company thousands or even millions of dollars in lost productivity and repair costs. The overall efficiency gains achieved through centralized management and automated processes ultimately contribute to a return on investment.
Clarifying Questions
Rmm for internal it department – What are the typical costs associated with implementing RMM solutions?
RMM costs vary significantly depending on the chosen solution, features, number of devices managed, and support packages. It’s crucial to get detailed pricing information from vendors and consider long-term costs.
How does RMM improve security in an internal IT environment?
RMM facilitates centralized security management, enabling proactive monitoring, remote patching, and access control. This allows IT teams to quickly identify and respond to potential threats, thereby enhancing the overall security posture.
What are some common challenges in integrating RMM with existing IT infrastructure?
Compatibility issues with existing systems, data migration complexities, and training requirements are some of the common integration challenges. Thorough planning and vendor consultation are essential for successful integration.
How can I choose the right RMM solution for my internal IT needs?
Consider your budget, the number of devices to manage, required features, and vendor reputation. Thorough research, vendor comparisons, and potentially pilot programs are recommended to find the optimal solution.